What is Blended Teaching and Learning?
Blended teaching is an approach that combines online and in–person instruction with asynchronous and synchronous instruction. It typically involves students engaging with course material online and coming together for in–person activities such as discussions, group work, and hands–on learning. The purpose of blended teaching is to combine the best of both worlds to create an engaging, interactive learning experience for students.
Face-to-Face Components of Blended Learning:
The goal of in–person class time is to provide students with an immersive and interactive learning experience. This includes engaging in discussion, working on projects together, and receiving instructor feedback. In–person class time also provides students with an opportunity to form relationships with classmates, ask questions, and benefit from the expertise of the instructor.
Online Components of Blended Learning:
The goal of online coursework is to provide students with the same educational opportunities that they might receive in a traditional classroom, but with the flexibility to engage remotely. This can include access to narrated or live-streamed lectures, assignments, resources, and assessments, as well as the ability to interact with instructors and other students. Online coursework also provides students with the opportunity to learn and practice 21st-century skills such as online collaboration, communication, problem-solving, and critical thinking using digital tools.
Digital tools are utilized to:
- Create online instructional activities that elicit discussions before a face-to-face class meeting.
- Extend a face-to-face class meeting discussion to the online environment.
- Facilitate activities and assessments.
- Facilitate a student research project.
- Provide group areas for students to work on team projects.
- conduct fieldwork.
- Engage and prepare students for face-to-face interaction.
Models of Blended Learning:
In any blended learning classroom, learning should be engaging and flexible to meet various needs. Additionally, online learning should be used in purposeful ways that support and drive bigger learning objectives. First, the “traditional” instructional model must be changed up, then the technology comes in acting as an “enabler to high-quality learning experiences” versus “driving” it, to support blended learning. Examples of the most common types of blended learning models are:
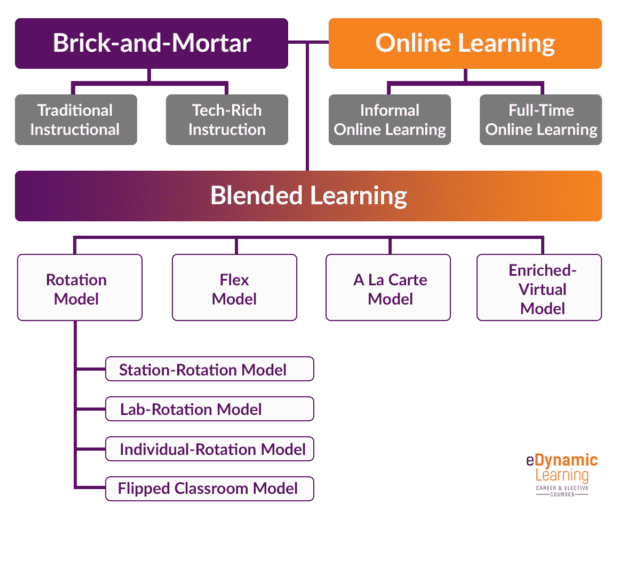
For more information on the Flipped Classroom model, visit our Flipped Learning website.
Quality Blended Course Review Rubric:
Based upon the Faculty Senate’s Best Practices in Web-Enhanced, Blended, and Online Teaching guidelines, the Quality Blended Course Rubric can be utilized as a tool to assess how core best practices are being followed; to ensure an effective learning experience for students. The rubric is formative rather than evaluative. The overall goal is to engage in a collaborative conversation regarding a course site and to assist with ongoing revisions and improvements to the course design and execution.
Devising a Blended Plan:
The key to successfully teaching a Blended or hybrid course is planning. Instructional Development specializes in working with faculty to assess course goals, inventory resources, and activities, as well as develop assessments for any course duration. Since designing a blended course plan is truly a customized process so we encourage faculty to schedule a consultation with one of our instructional designers to get started. It is helpful to have a syllabus and key course goals in mind before the appointment.
Blended Training Options:
- Register for an upcoming certification course or workshop on blended teaching.
- Submit a Blended Teaching Profile to be considered for bypassing the blended training requirement if you have prior Blended teaching experience and a comparable certification.
